Botnets
DOS Attacks
July 20, 2014
Phlashing-PDOS
July 20, 2014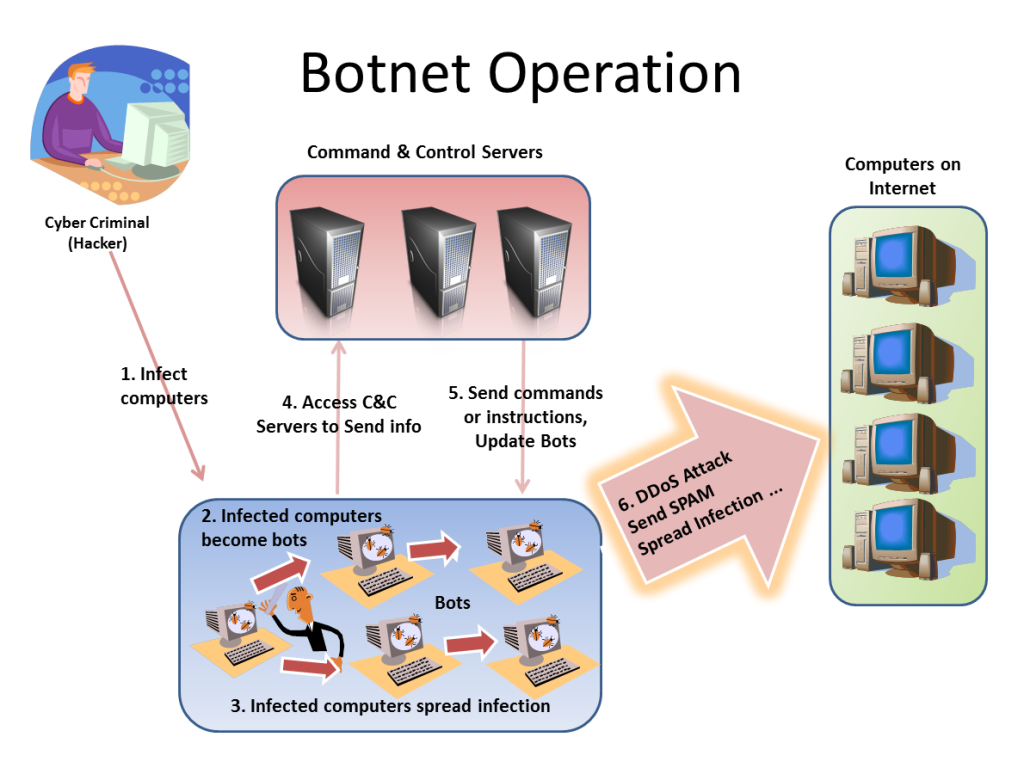
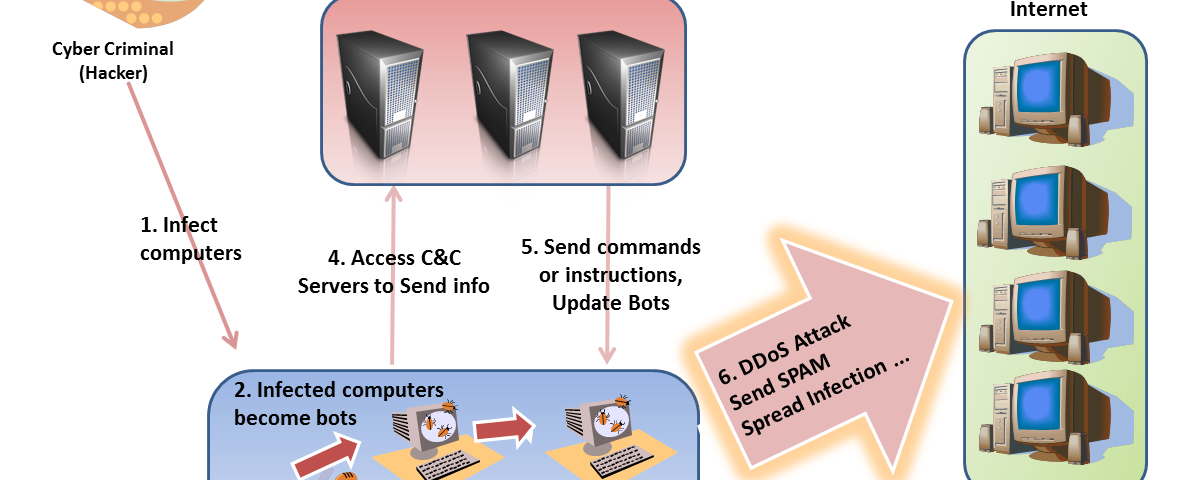
A botnet or robot network is a group of computers running a computer application controlled and manipulated only by the owner or the software source. The botnet may refer to a legitimate network of several computers that share program processing amongst them.
Usually though, when people talk about botnets, they are talking about a group of computers infected with the malicious kind of robot software, the bots, which present a security threat to the computer owner. Once the robot software (also known as malicious software or malware) has been successfully installed in a computer, this computer becomes a zombie or a drone, unable to resist the commands of the bot commander.
A botnet may be small or large depending on the complexity and sophistication of the bots used. A large botnet may be composed of ten thousand individual zombies. A small botnet, on the other hand may be composed of only a thousand drones. Usually, the owners of the zombie computers do not know that their computers and their computers’ resources are being remotely controlled and exploited by an individual or a group of malware runners through Internet Relay Chat (IRC)
There are various types of malicious bots that have already infected and are continuing to infect the internet. Some bots have their own spreaders – the script that lets them infect other computers (this is the reason why some people dub botnets as computer viruses) – while some smaller types of bots do not have such capabilities.
Different Types of Bots
Here is a list of the most used bots in the internet today, their features and command set.
XtremBot, Agobot, Forbot, Phatbot
These are currently the best known bots with more than 500 versions in the internet today. The bot is written using C++ with cross platform capabilities as a compiler and GPL as the source code. These bots can range from the fairly simple to highly abstract module-based designs. Because of its modular approach, adding commands or scanners to increase its efficiency in taking advantage of vulnerabilities is fairly easy. It can use libpcap packet sniffing library, NTFS ADS and PCRE. Agobot is quite distinct in that it is the only bot that makes use of other control protocols besides IRC.
UrXBot, SDBot, UrBot and RBot
Like the previous type of bot, these bots are published under GPL, but unlike the above mentioned bots these bots are less abstract in design and written in rudimentary C compiler language. Although its implementation is less varied and its design less sohisticated, these type of bots are well known and widely used in the internet.
GT-Bots and mIRC based bots
These bots have many versions in the internet mainly because mIRC is one of the most used IRC client for windows. GT stands for global threat and is the common name for bots scripted using mIRC. GT-bots make use of the mIRC chat client to launch a set of binaries (mainly DLLs) and scripts; their scripts often have the file extensions .mrc.
Malicious Uses of Botnets
Types Of Botnet Attack
Denial of Service Attacks
A botnet can be used as a distributed denial of service weapon. A botnet attacks a network or a computer system for the purpose of disrupting service through the loss of connectivity or consumption of the victim network’s bandwidth and overloading of the resources of the victim’s computer system. Botnet attacks are also used to damage or take down a competitor’s website.
Fast flux is a DNS technique used by botnets to hide phishing and malware delivery sites behind an ever-changing network of compromised hosts acting as proxies.
Any Internet service can be a target by botnets. This can be done through flooding the website with recursive HTTP or bulletin-board search queries. This mode of attack in which higher level protocols are utilized to increase the effects of an attack is also termed as spidering.
Spyware
Its a software which sends information to its creators about a user’s activities – typically passwords, credit card numbers and other information that can be sold on the black market. Compromised machines that are located within a corporate network can be worth more to the bot herder, as they can often gain access to confidential information held within that company. There have been several targeted attacks on large corporations with the aim of stealing sensitive information, one such example is the Aurora botnet.
Adware
Its exists to advertise some commercial entity actively and without the user’s permission or awareness, for example by replacing banner ads on web pages with those of another content provider.
Spamming and Traffic Monitoring
A botnet can also be used to take advantage of an infected computer’s TCP/IP’s SOCKS proxy protocol for networking appications. After compromising a computer, the botnet commander can use the infected unit (a zombie) in conjunction with other zombies in his botnet (robot network) to harvest email addresses or to send massive amounts of spam or phishing mails.
Moreover, a bot can also function as a packet sniffer to find and intercept sensitive data passing through an infected machine. Typical data that these bots look out for are usernames and passwords which the botnet commander can use for his personal gain. Data about a competitor botnet installed in the same unit is also mined so the botnet commander can hijack this other botnet.
Access number replacements are where the botnet operator replaces the access numbers of a group of dial-up bots to that of a victim’s phone number. Given enough bots partake in this attack, the victim is consistently bombarded with phone calls attempting to connect to the internet. Having very little to defend against this attack, most are forced into changing their phone numbers (land line, cell phone, etc.).
Keylogging and Mass Identity Theft
An encryption software within the victims’ units can deter most bots from harvesting any real information. Unfortunately, some bots have adapted to this by installing a keylogger program in the infected machines. With a keylogger program, the bot owner can use a filtering program to gather only the key sequence typed before or after interesting keywords like PayPal or Yahoo mail. This is one of the reasons behind the massive PayPal accounts theft for the past several years.
Bots can also be used as agents for mass identity theft. It does this through phishing or pretending to be a legitimate company in order to convince the user to submit personal information and passwords. A link in these phishing mails can also lead to fake PayPal, eBay or other websites to trick the user into typing in the username and password.
Botnet Spread
Botnets can also be used to spread other botnets in the network. It does this by convincing the user to download after which the program is executed through FTP, HTTP or email.
Pay-Per-Click Systems Abuse
Botnets can be used for financial gain by automating clicks on a pay-per-click system. Compromised units can be used to click automatically on a site upon activation of a browser. For this reason, botnets are also used to earn money from Google’s Adsense and other affiliate programs by using zombies to artificially increase the click counter of an advertisement.